How to calculate pipe laser reading?
Posted by Philip Hanrahan B.E., B.A., M.I.E.I. on 28th Feb 2021
What is a pipe laser and how does it work?
A pipe laser is a type of construction laser that is used to measure and determine the correct grade for pipes. It makes grade calculations in sewer, wastewater and other linear pipe runs a lot easier.
Pipe lasers provide ease of operation and computerized self-calibration that can speed pipe laying. They directly determine your pipe grade and help you to handle all the tricks and exceptions that arise when you are installing sewer pipe and other lines.
Pipe lasers shoot a high-powered beam of light at a predetermined angle to establish the appropriate grade of a construction project. Standard pipe grade setting involves determining the length of pipe, the depth to the invert and details such as any protrusion into manholes. Ensuring you have accurate and appropriate numbers, you can calculate the change in depth of the pipe invert over the length of the pipe and derive a grade percentage from that.
How to calculate pipe laser reading?
A pipe grade is the incline or decline at which a pipe is set, and is expressed as a percentage. The grade of the pipe helps manage liquid flow in underground construction projects. This percentage is calculated by dividing the elevation difference by the run of pipe.
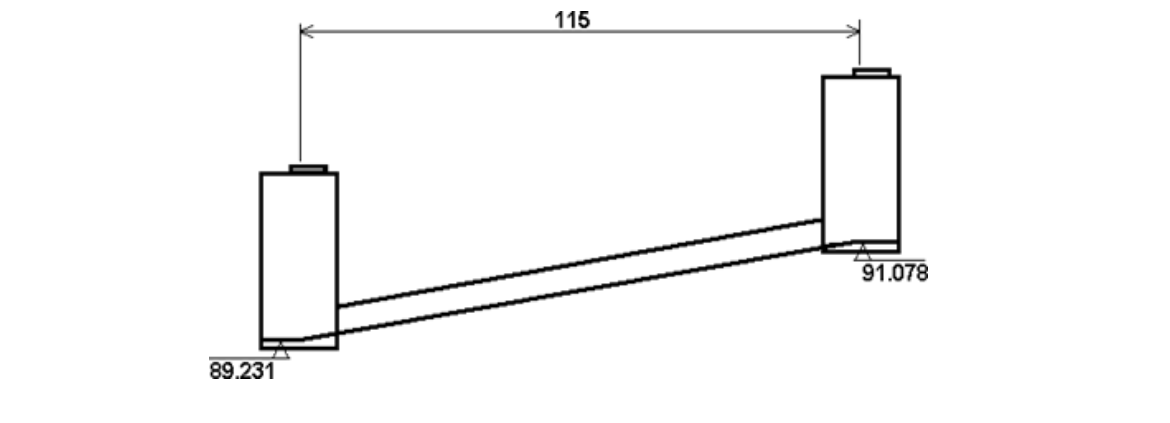
If the gradient between the manholes is given in rise/fall or as a ratio, calculate the laser reading as follows:

Things to remember:
1. If the rise/ratio is given as 1 in 85 make sure that both dimensions are the same
e.g. 1” in 240” NOT 1” in20’
0.150m in 30m NOT 150mm in 30m
150mm in 3000mm NOT 150mm in 30m
2. + grades always RISE away from the laser

- grades always FALL away from the laser
3. When using the LASER CONVERSION CHART read the Rise/Ratio (e.g. 1:85) from the LEFT hand column and the corresponding Pipe Laser Reading (1.176) from the RIGHT hand column.
Potential outside sources of error
- During pipe laying, logging in the pipe may be encountered leading to refraction of the laser beam. Since the beam appears to drift, the operator is likely to think that something is wrong with the instrument. This refraction problem can be solved by placing a fan at one end of the pipe to keep it clear.
- Retraction caused by heat and particles in the air can also be a problem when using a rotating laser beam, especially at extended distances. To give you an example, a reading error of up to 6mm can be caused by refraction and the curvature of the earth at as little as 300 meters range.
- Reflections can result in incorrect signals to the laser detector. Glass-walled buildings can cause such reflections. This problem can be prevented by shielding the building from the beam with a blind mounted on the instrument.
- Other factors which can affect the laser beam are heavy rain, fog or snowfall - water and ice particles in the air can lead to incorrect readings.
Pipe lasers can make a huge difference in overall cost project by saving time and ensuring highest accuracy.
Pipe lasers are designed to help with specific pipe installation challenges, including long linear runs of supply or waste pipe. They don’t eliminate the need for skilled personnel to ensure that the overall installation is true and correct, but they can make a large difference in overall project costs and accuracy and can let pipe installation personnel perform their own measurements easily on smaller projects.
---
Download our handy Laser Conversion Chart.
Hire pipe laser at a great rate from our Hire Shop.


